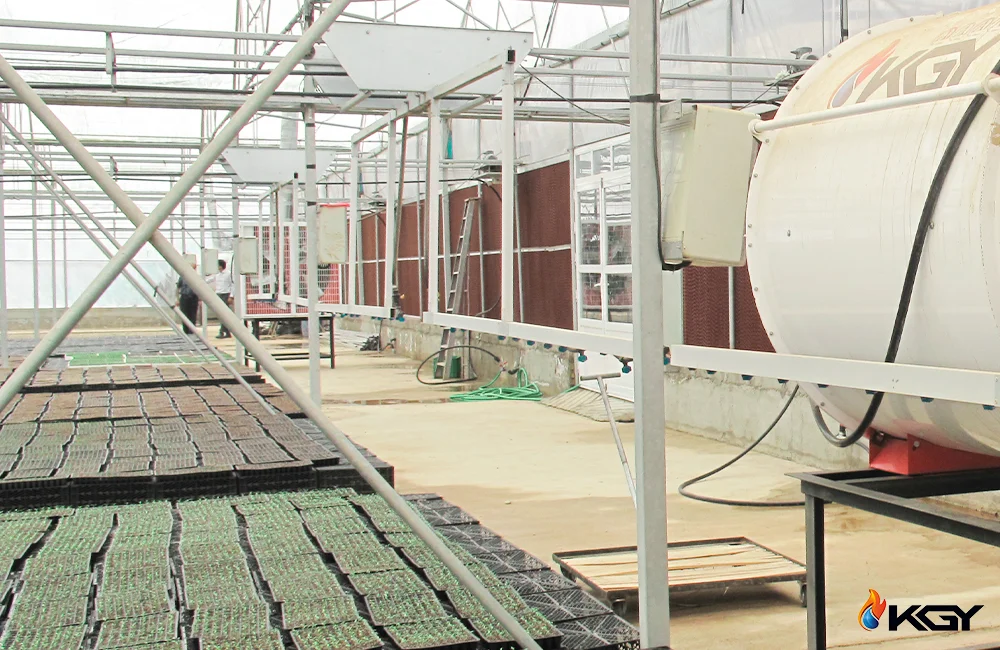
In the bustling world of agriculture, where precision is the key to reaping bountiful harvests, one often overlooked factor stands tall – temperature control. Picture this: a greenhouse where the delicate balance between heat and coolness can mean the difference between flourishing crops and withering dreams. As the heartbeat of successful cultivation, maintaining an optimal temperature is paramount. And in this symphony of agricultural perfection, the greenhouse pad cooling system emerges as the maestro.
Gone are the days of sweating over soaring temperatures inside your greenhouse. The greenhouse pad cooling system, a game-changing innovation, not only tackles the heat conundrum but does so with finesse and efficiency. Join us on a journey into the heart of this revolutionary cooling solution, where science meets horticulture in perfect harmony. Discover how it has become the go-to choice for farmers worldwide, transforming the way we cultivate and nurture our green treasures.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Greenhouse Pad Cooling System?
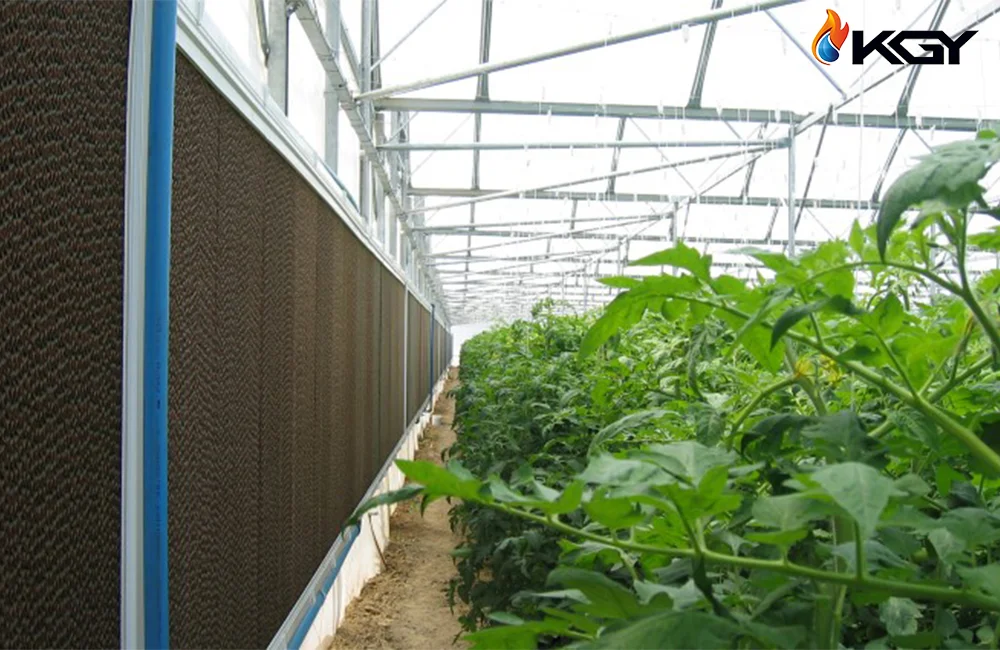

A Greenhouse Pad Cooling System is a sophisticated climate control mechanism designed to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels within a greenhouse environment. As an innovative solution to combat the challenges of excessive heat, this system utilizes the principles of evaporative cooling to create a conducive atmosphere for plant growth.
How it Works:
The heart of the greenhouse pad cooling system lies in the process of evaporation. The system comprises porous evaporative cooling pads strategically installed at one end of the greenhouse. These pads are made from specialized cellulose material designed to absorb and retain water.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Water Circulation: A water distribution system ensures a continuous flow of water over the surface of the cooling pads.
- Airflow: As ambient air is drawn through the wet pads by fans strategically placed at the opposite end of the greenhouse, the water on the surface evaporates.
- Evaporative Cooling: The process of evaporation is inherently cooling, causing the temperature of the air passing through the wet pads to drop significantly.
- Cooled Air Distribution: The now-cooled air is evenly distributed throughout the greenhouse, effectively lowering the overall temperature and creating an optimal environment for plant growth.
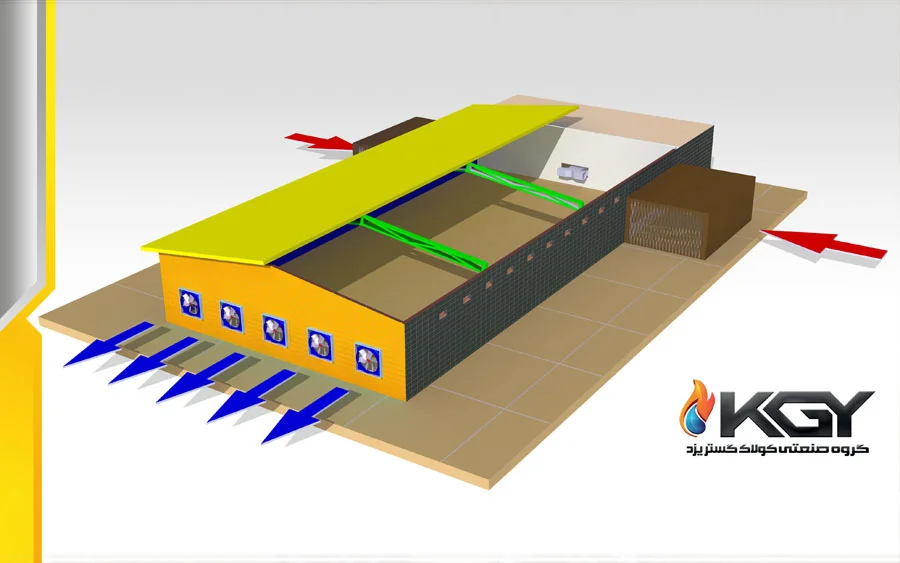
Key Components and Their Functions:
- Evaporative Cooling Pads: The cellulose pads serve as the primary medium for water evaporation, promoting efficient cooling.
- Water Distribution System: A network of pipes and nozzles evenly distributes water across the surface of the cooling pads.
- Fans: Strategically placed fans draw warm air through the wet pads, facilitating the evaporative cooling process.
- Control System: An automated control system regulates the operation of the pad cooling system based on preset temperature and humidity parameters, ensuring precise climate control.
The Science Behind Pad Cooling in Greenhouses:
At its core, pad cooling leverages the fundamental principles of thermodynamics and evaporative cooling. When water evaporates, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air, causing a drop in temperature. This cooling effect is harnessed to create an environment that mirrors the ideal conditions for plant growth.
As warm air passes through the wet cooling pads, water evaporates, and the air temperature decreases. This cooled air is then circulated within the greenhouse, providing a refreshing and controlled climate. The efficiency of the system lies in its ability to balance temperature and humidity, fostering an optimal setting for plants to thrive. Greenhouse pad cooling systems exemplify the synergy between science and agriculture, demonstrating how innovation can enhance the cultivation process in a sustainable and effective manner.
Benefits of Greenhouse Pad Cooling:
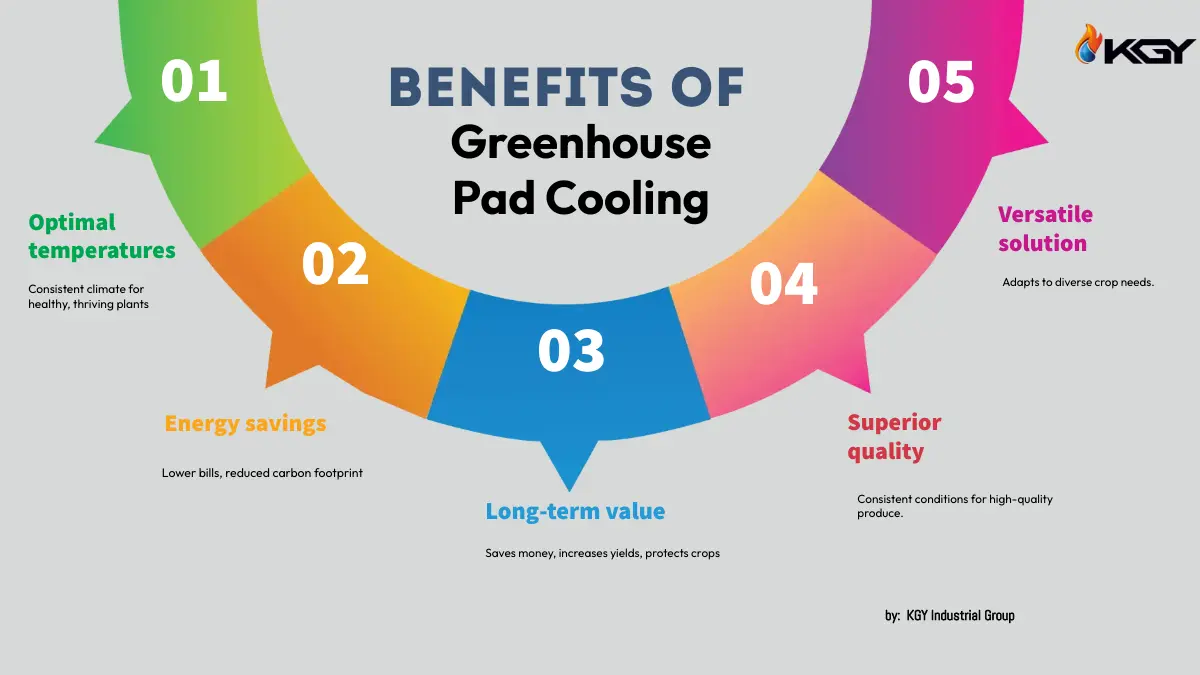
In the ever-evolving landscape of agricultural technology, greenhouse pad cooling systems have emerged as a beacon of innovation, offering a multitude of advantages that transcend traditional climate control methods. Let's explore the tangible benefits that make these systems a game-changer for greenhouse cultivators.
Improved Plant Growth:
- Ensured optimal temperature regulation fosters consistent and favorable conditions for plant growth.
- Enhanced photosynthesis in an ideal environment contributes to healthier and more robust crops.
Energy Efficiency:
- Marked reduction in energy consumption compared to traditional cooling methods.
- Environmentally friendly practices aligning with sustainability goals and minimizing the carbon footprint.
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Long-term savings become apparent through lower energy bills, increased crop yields, and reduced maintenance costs.
- Mitigation of crop losses due to heat stress adds to the overall cost-effectiveness of the system.
Enhanced Crop Quality:
- Consistent environmental conditions ensure high-quality, market-ready produce.
- Controlled humidity levels reduce disease pressure, safeguarding the quality of the harvest.
Adaptability to Various Crops:
- Versatility allows for the customization of environments tailored to the specific needs of different crops.
How to Install a Greenhouse Pad Cooling System
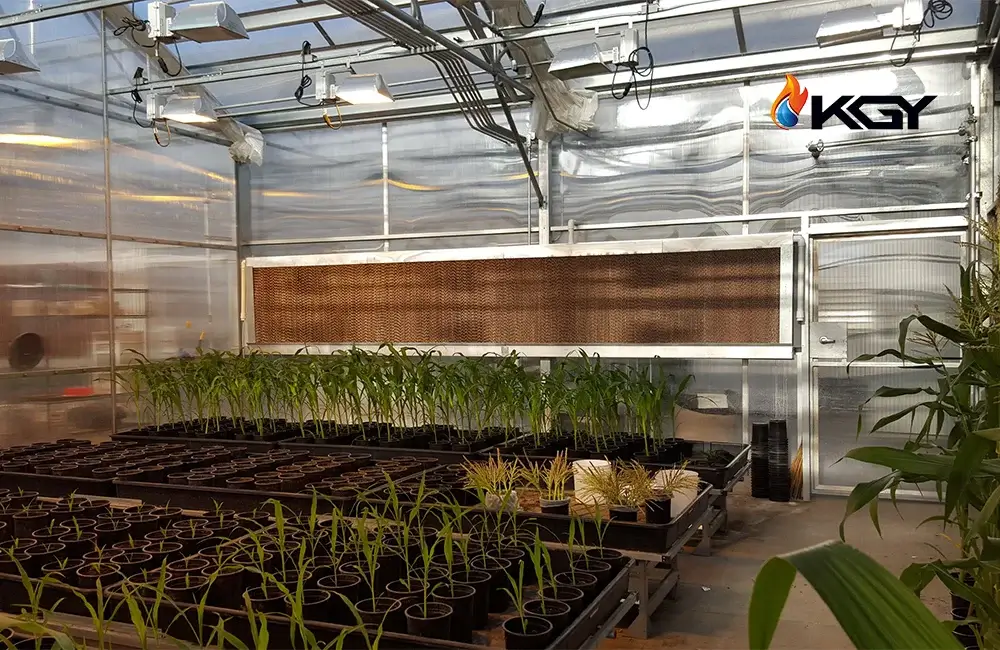

Installing a greenhouse pad cooling system involves a systematic approach to ensure optimal performance. Here's a condensed overview of the installation process:
Materials and Tools:
Ensure you have the necessary materials and tools, including a greenhouse pad cooling system kit, measuring tape, power drill, pliers, wrenches, PVC pipes, hose, water source, level, mounting brackets, duct tape, and safety gear.
Step 1: Plan the Layout:
Evaluate the greenhouse layout, considering factors like wind, sunlight, and airflow. Determine optimal placements for cooling pads and fans.
Step 2: Install Cooling Pads:
Attach cooling pads evenly within the greenhouse, securing them with mounting brackets for stability.
Step 3: Set Up Water Distribution:
Connect pipes and fittings for the water distribution system, ensuring even water distribution across cooling pads.
Step 4: Mount Fans:
Install fans on the opposite end of the greenhouse from cooling pads. Secure them with mounting brackets for proper airflow.
Step 5: Connect Power Supply:
Connect fans and electrical components to a reliable power source following safety guidelines and local codes.
Step 6: Set Up Control System:
Install and program the control system for temperature and humidity regulation. Strategically place sensors for accurate readings.
Step 7: Test the System:
Run a system test to ensure proper fan and water distribution. Adjust control settings as needed for desired climate conditions.
Step 8: Fine-Tuning and Calibration:
Periodically monitor and make adjustments based on greenhouse conditions. Regularly calibrate the control system for optimal performance.
Best Practices and Tips:
- Schedule routine maintenance, including cleaning cooling pads and checking for clogs.
- Use clean water to prevent clogs and extend cooling pad lifespan.
- Ensure proper ventilation to expel warm air and prevent humidity buildup.
- Make seasonal adjustments to system settings for varying weather conditions.
- Seek professional assistance if unsure about any installation aspect.
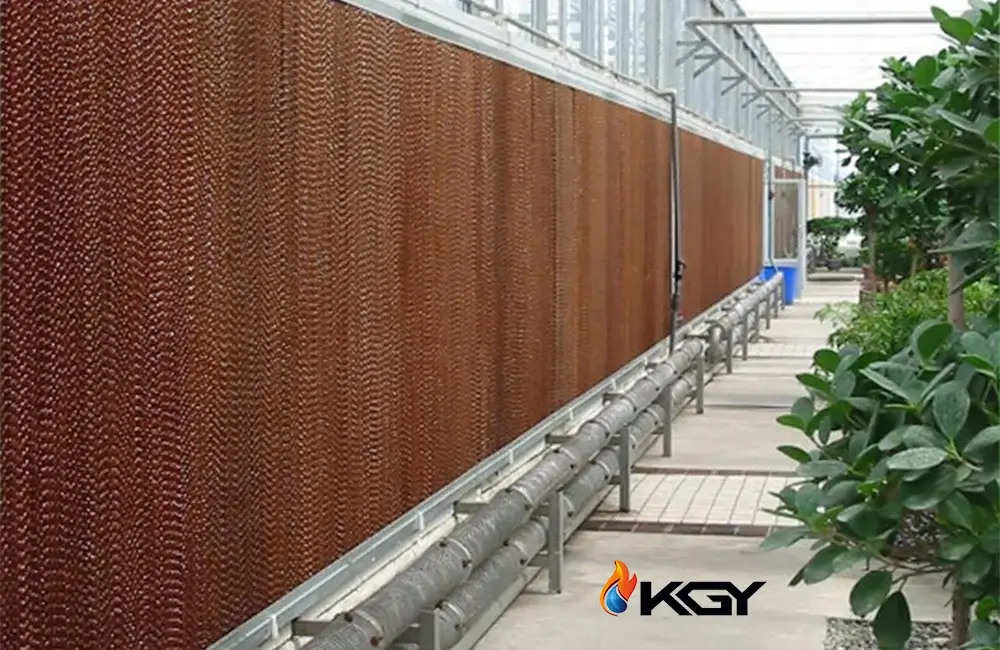

Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Greenhouse Pad Cooling Systems
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of a greenhouse pad cooling system requires a systematic approach to routine maintenance and proactive troubleshooting. Here's a condensed overview:
Routine Maintenance Tasks:
Clean Cooling Pads:
- Regularly remove dust and dirt from evaporative cooling pads to maintain efficiency.
Inspect Water Distribution System:
- Check for clogs and ensure even water distribution across the pads.
Monitor Fan Operation:
- Regularly inspect and clean fans, ensuring smooth operation and optimal airflow.
Calibrate Control System:
- Periodically calibrate the control system for accurate temperature and humidity regulation.
Check Electrical Connections:
- Inspect and tighten electrical connections, replacing damaged wiring.
Inspect Structural Components:
- Ensure the structural integrity of mounting brackets, frames, and components.
Evaluate Water Quality:
- Monitor water quality to prevent mineral buildup in the distribution system.
Troubleshooting Tips for Common Issues:
Insufficient Cooling:
- Check for clogged cooling pads, uneven water distribution, or incorrect fan settings.
Uneven Cooling:
- Inspect the water distribution system, cooling pads, and adjust fan placement for even airflow.
- Water Leaks:
- Inspect pipes and fittings for leaks, tightening loose connections.
- Fan Issues:
- Address unusual noises or vibrations, check for obstructions, and inspect electrical connections.
- Control System Malfunctions:
- Verify power supply, calibrate sensors, and update software or firmware if needed.
Importance of Regular Checks and Preventive Measures:
- Prevent Downtime: Regular maintenance identifies potential issues, minimizing system downtime.
- Optimize Performance: Proactive care ensures peak efficiency for optimal climate control.
- Extend Lifespan: Routine maintenance extends the lifespan of components, reducing replacement costs.
- Energy Efficiency: Well-maintained systems operate efficiently, lowering energy consumption.
- Maximize Crop Yield: Consistent optimal conditions contribute to higher crop yields and quality.
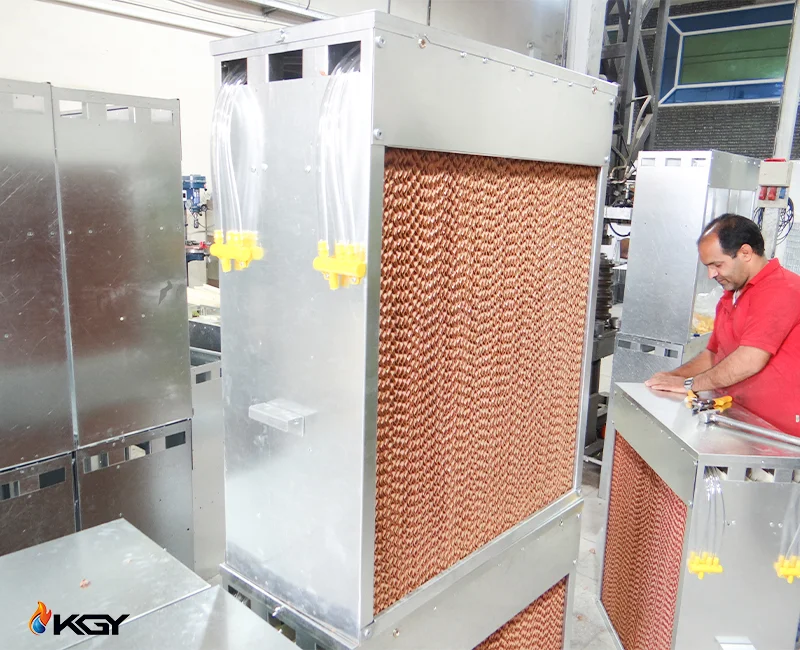

Comparison of Greenhouse Pad Cooling System with Alternative Cooling Methods
Greenhouse pad cooling systems demonstrate clear advantages over alternative cooling methods, making them a preferred choice for many greenhouse operators. Here's a condensed overview of the comparison:
Pad Cooling vs. Fan Ventilation:
Advantages of Pad Cooling:
- Enhanced cooling efficiency through evaporation.
- Better humidity control.
- Lower energy consumption compared to fan ventilation.
Pad Cooling vs. Shade Netting:
Advantages of Pad Cooling:
- Actively lowers greenhouse temperature.
- Versatile for year-round use.
Pad Cooling vs. High-Pressure Fogging:
Advantages of Pad Cooling:
- Lower energy consumption.
- More even and widespread cooling.
Pad Cooling vs. Air Conditioning:
Advantages of Pad Cooling:
- Cost-effectiveness in installation and operation.
- Sustainability through reliance on evaporation.
Pad Cooling vs. Exhaust Fans:
Advantages of Pad Cooling:
- Increased cooling capacity for larger greenhouses.
- Improved humidity control.
Pad Cooling vs. Misting Systems:
Advantages of Pad Cooling:
- Greater energy efficiency.
- Reduced wetness on surfaces.
Read More: Greenhouse Heating Systems
Key Advantages Setting Pad Cooling Systems Apart:
Energy Efficiency:
- Reliance on the natural process of evaporation ensures energy efficiency.
Humidity Control:
- Effective control of humidity levels, creating an optimal environment for plant growth.
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Economical initial investment and operational costs contribute to long-term savings.
Versatility:
- Adaptability to various greenhouse sizes and configurations for versatile use.
Even Cooling Distribution:
- Provides a more even and widespread cooling effect throughout the greenhouse.
Environmental Impact of Greenhouse Pad Cooling Systems

Greenhouse pad cooling systems champion several environmental benefits, fostering sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practices. The use of evaporative cooling principles in these systems brings forth the following key advantages:
Reduced Energy Consumption:
- Natural evaporation process leads to significantly lower energy consumption compared to mechanical cooling methods.
- Contributes to decreased electricity demand and reduces associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Minimized Carbon Footprint:
- Lower energy requirements result in reduced greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Choosing pad cooling over conventional systems supports a more sustainable agricultural practice.
Water Efficiency:
- Efficient water usage through evaporation minimizes water consumption while providing effective temperature control.
- Aligns with sustainable water management practices in agriculture.
Less Reliance on Refrigerants:
- Avoidance of harmful refrigerants used in some conventional cooling systems.
- Contributes to ozone layer protection and reduction of environmental impacts associated with refrigerant use.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices:
- The system's efficient cooling and humidity control support balanced and controlled growing environments.
- Allows adaptability to renewable energy sources for further environmental minimization.
Long-Term Environmental Benefits:
- Economic benefits, coupled with system longevity, contribute to long-term environmental sustainability.
- Positive influence on the industry towards adopting greener and more sustainable approaches.

Cost Analysis of Greenhouse Pad Cooling Systems
Investing in a greenhouse pad cooling system entails initial costs and promises long-term savings. The breakdown includes:
Initial Costs:
- Components like cooling pads, fans, water distribution, and control systems.
- Installation expenses for labor and additional materials.
- Infrastructure for a reliable water source.
- Maintenance tools.
Potential Long-Term Savings:
- Energy efficiency leads to lower electricity bills.
- Improved crop yields contribute to increased revenue.
- Reduced maintenance costs and longer system lifespan.
- Efficient water usage results in lower water costs.
- Possible financial benefits through environmental incentives.
Return on Investment (ROI):
Calculated as [(Net Gain - Initial Investment) / Initial Investment] 100.
Net Gain is the difference between total long-term savings and initial costs.
Example scenario: ROI of 60% over ten years for a $50,000 investment.
Considerations:
- Regional factors such as energy costs and incentives.
- System efficiency and proper maintenance practices.
- Crop value as a determinant of economic impact.
In conclusion, the adoption of greenhouse pad cooling systems signifies a pivotal shift toward sustainable, energy-efficient, and cost-effective agriculture. The benefits extend beyond economic gains to encompass environmental conservation and improved crop quality, aligning with the global push towards greener practices.
As you embark on your journey in the world of greenhouse cultivation or if you're already utilizing pad cooling systems, we invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and insights. Have you witnessed the transformative impact of pad cooling on your crops? Are there specific challenges you've encountered or innovative practices you've implemented?
Key Advantages Setting Pad Cooling Systems Apart:
Energy Efficiency:
- Reliance on the natural process of evaporation ensures energy efficiency.
Humidity Control:
- Effective control of humidity levels, creating an optimal environment for plant growth.
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Economical initial investment and operational costs contribute to long-term savings.
Versatility:
- Adaptability to various greenhouse sizes and configurations for versatile use.
Even Cooling Distribution:
- Provides a more even and widespread cooling effect throughout the greenhouse.
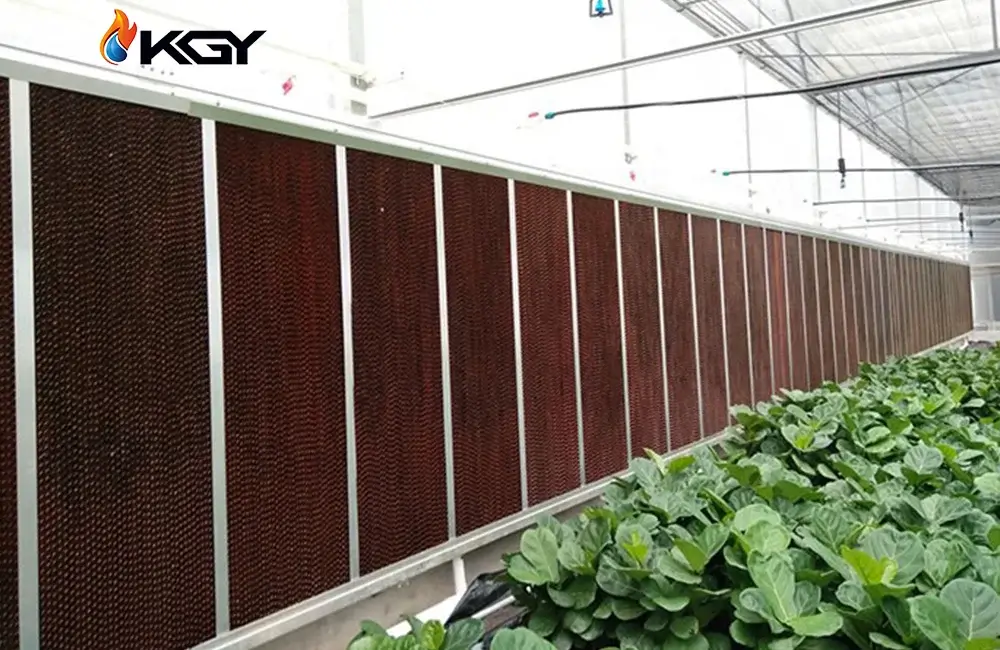

Environmental Impact of Greenhouse Pad Cooling Systems
Greenhouse pad cooling systems champion several environmental benefits, fostering sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practices. The use of evaporative cooling principles in these systems brings forth the following key advantages:
Reduced Energy Consumption:
- Natural evaporation process leads to significantly lower energy consumption compared to mechanical cooling methods.
- Contributes to decreased electricity demand and reduces associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Minimized Carbon Footprint:
- Lower energy requirements result in reduced greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Choosing pad cooling over conventional systems supports a more sustainable agricultural practice.
Water Efficiency:
- Efficient water usage through evaporation minimizes water consumption while providing effective temperature control.
- Aligns with sustainable water management practices in agriculture.
Less Reliance on Refrigerants:
- Avoidance of harmful refrigerants used in some conventional cooling systems.
- Contributes to ozone layer protection and reduction of environmental impacts associated with refrigerant use.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices:
- The system's efficient cooling and humidity control support balanced and controlled growing environments.
- Allows adaptability to renewable energy sources for further environmental minimization.
Long-Term Environmental Benefits:
- Economic benefits, coupled with system longevity, contribute to long-term environmental sustainability.
- Positive influence on the industry towards adopting greener and more sustainable approaches.
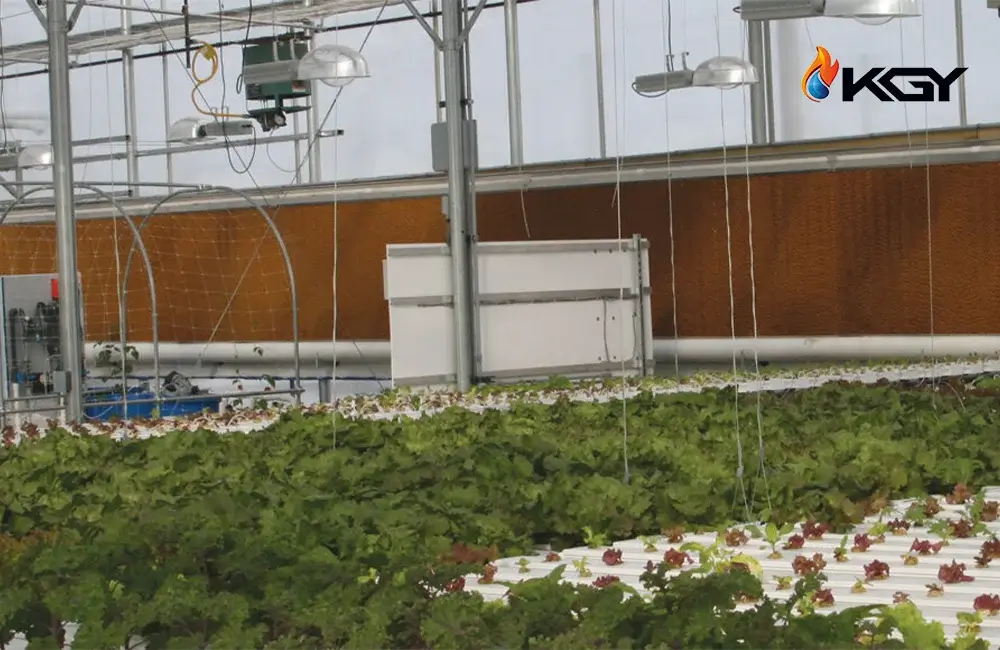

Cost Analysis of Greenhouse Pad Cooling Systems
Investing in a greenhouse pad cooling system entails initial costs and promises long-term savings. The breakdown includes:
Initial Costs:
- Components like cooling pads, fans, water distribution, and control systems.
- Installation expenses for labor and additional materials.
- Infrastructure for a reliable water source.
- Maintenance tools.
Potential Long-Term Savings:
- Energy efficiency leads to lower electricity bills.
- Improved crop yields contribute to increased revenue.
- Reduced maintenance costs and longer system lifespan.
- Efficient water usage results in lower water costs.
- Possible financial benefits through environmental incentives.
Return on Investment (ROI):
Calculated as [(Net Gain - Initial Investment) / Initial Investment] 100.
Net Gain is the difference between total long-term savings and initial costs.
Example scenario: ROI of 60% over ten years for a $50,000 investment.
Considerations:
- Regional factors such as energy costs and incentives.
- System efficiency and proper maintenance practices.
- Crop value as a determinant of economic impact.
In conclusion, the adoption of greenhouse pad cooling systems signifies a pivotal shift toward sustainable, energy-efficient, and cost-effective agriculture. The benefits extend beyond economic gains to encompass environmental conservation and improved crop quality, aligning with the global push towards greener practices.
As you embark on your journey in the world of greenhouse cultivation or if you're already utilizing pad cooling systems, we invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and insights. Have you witnessed the transformative impact of pad cooling on your crops? Are there specific challenges you've encountered or innovative practices you've implemented?
Frequently Asked Questions
It's a technology using evaporative cooling with wetted pads and fans to regulate temperature and humidity for optimal plant growth.
Air is drawn through wetted cooling pads, causing water to evaporate and cool the air, which is then circulated inside the greenhouse.
Evaporative cooling pads, fans, water distribution system, control system with sensors, and additional equipment like filters and pumps.
Improved plant growth, energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, enhanced crop quality, adaptability, and reduced environmental impact.
Involves strategic placement of cooling pads, setting up water distribution, installing fans, connecting the control system, and following manufacturer guidelines.
Routine cleaning of cooling pads, inspecting and cleaning the water system, checking fans, calibrating the control system, and ensuring overall functionality.
Check for clogged pads, ensure even water distribution, inspect fans, verify electrical connections, and calibrate sensors systematically.